Composite Index
Composite Index is a widely used multi-indicator evaluation method. It converts multiple indicators into a single composite index to assess the overall situation of a given subject. It is located in SPSSAU -> Comprehensive Evaluation -> Composite Index.
SPSSAU Operations
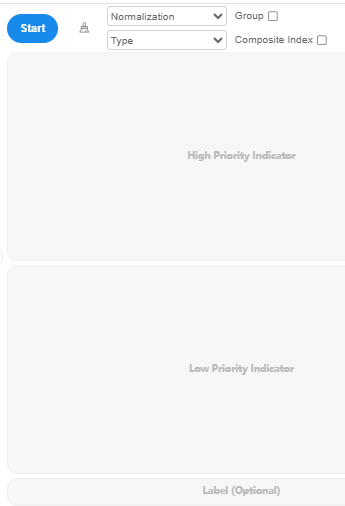
To conduct the analysis, drag positive or negative indicators into the designated boxes and click 'Start'. You may also drag the 'research object' into the 'Label' box. SPSSAU provides four parameters.
Standardization Method: The default is 'Relative Standardization', but users can choose 'Positive Transformation' or No Processing.
Calculation Method: The default is 'Sum Between-group, Product Within-group'. Three other methods are available: 'Sum Between-group, Sum Within-group', 'Product Between-group, Sum Within-group', and 'Product Between-group, Product Within-group'.
Indicator Group: By default, all evaluation indicators belong to one group unless specified otherwise.
Composite Index: When selected, SPSSAU saves the composite index as a new title (e.g., 'comIndex_****').
SPSSAU Data Format
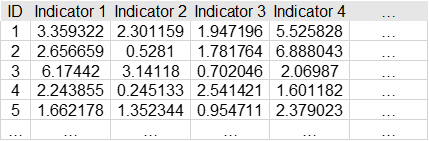
During Composite Index Calculation, one column represents the research object (if absent or not placed in the 'Label' box, SPSSAU will automatically name them Item 1, Item 2, Item 3, etc.). Each indicator occupies one column, regardless of whether it is a high-quality or low-quality indicator.
Algorithm
1.Indicator Standardization
SPSSAU provides two methods: 'Relative Standardization' and 'Positive Transformation'.
Relative Standardization:
For high-quality indicators:
For low-quality indicators:
Positive Transformation:
For high-quality indicators:
For low-quality indicators:
2.Define Groups
This step involves grouping research indicators into multiple categories. The user determines the grouping configuration. If left unconfigured, SPSSAU defaults to a single category for all indicators.
3.Calculate the Composite Index
The Comprehensive Index (I) involves both addition and multiplication methods, distinguishing within-group and between-group operations, resulting in four possible methods:
x represents the evaluation index data, y is the comprehensive index (within-group index) calculated for each group. m represents the number of indicators in a given group, and l represents the number of groups. Finally, the comprehensive index is obtained by combining four calculation methods as follows:
| Four Calculation Methods | |
|---|---|
| Calculation Method | Description |
| Sum Between-group, Sum Within-group | Indicators within a group are summed to obtain a within-group index, which is then summed between groups. |
| Sum Between-group, Product Within-group | Indicators within a group are multiplied to obtain a within-group index, which is then summed between groups. |
| Product Between-group, Sum Within-group | Indicators within a group are summed to obtain a within-group index, which is then multiplied between groups. |
| Product Between-group, Product Within-group | Indicators within a group are multiplied to obtain a within-group index, which is then multiplied between groups. |
References
【1】The SPSSAU project (2024). SPSSAU. (Version 24.0) [Online Application Software]. Retrieved from https://www.spssau.com.
【2】周俊,马世澎. SPSSAU科研数据分析方法与应用.第1版[M]. 电子工业出版社,2024.